|
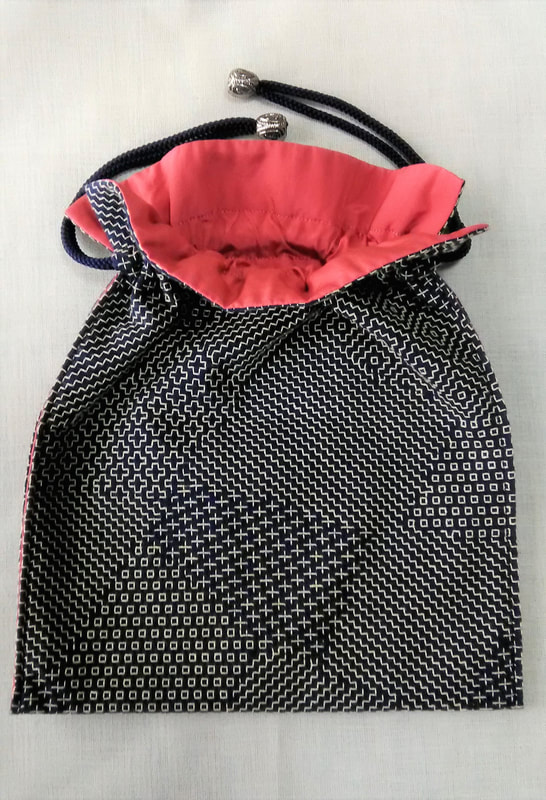
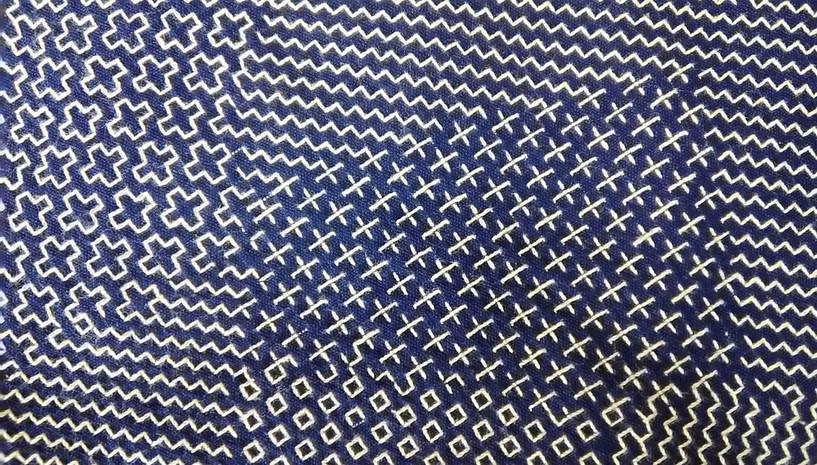
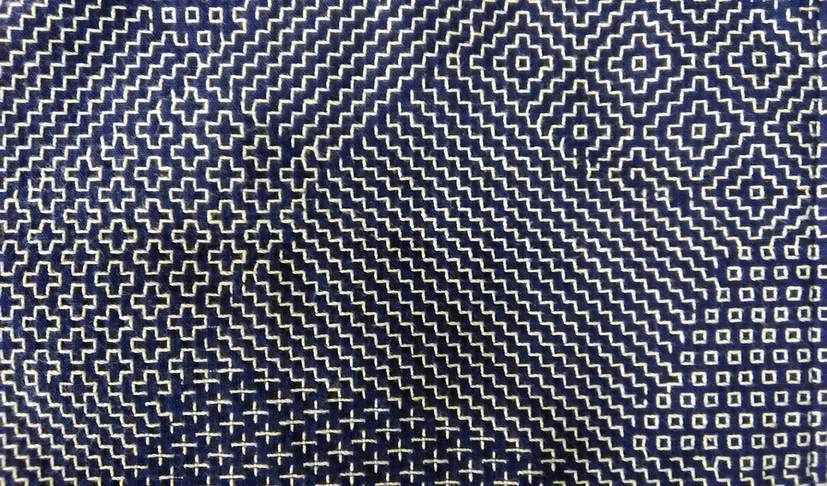
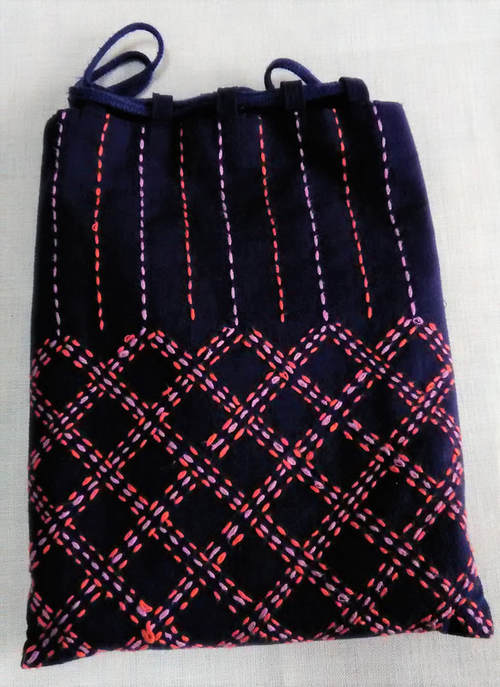
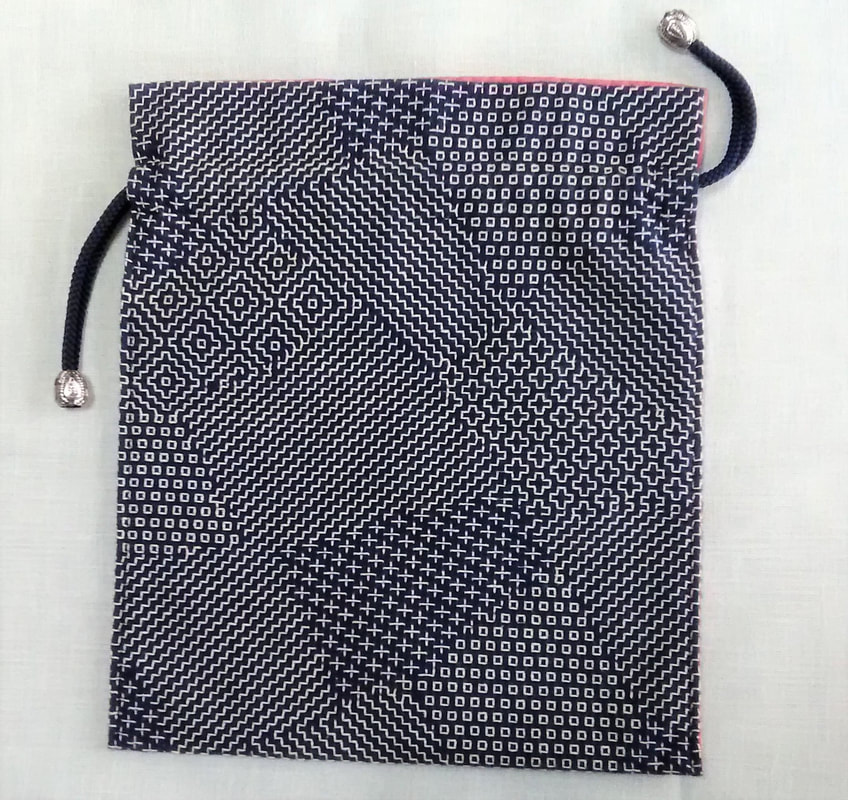
Imagine my delight when the postman delivered me a package recently, and I opened it up to find this gorgeous drawstring bag inside, a gift from an acquaintance who thought I could appreciate it. And she was right! I oohed and aahed with admiration as I examined it every from angle, resisting the temptation to unpick the beautiful red lining and peek at the underside. This type of bag, called a kinchaku in Japanese, was—and still is--used to carry around valuables or personal effects. Although an accessory for Japanese-style clothing, and probably not as common as it once used to be now that Western dress is the norm, it is nevertheless, far from having fallen out of use. I often see the elderly ladies in my neighborhood out for a daily walk clutching their kinchaku. And schoolchildren keep stationery, or implements for school lunches in these bags, though they are far more likely to be decorated with cute characters than sashiko. At summer festivals kinchaku are a common accessory for traditional festival wear, in fact I have a fancy red one to go with my yukata (cotton summer kimono). Naturally cloth kinchaku are ideal for sashiko, and the choice of pattern can indicate anything from seasonal themes to protection from evil spirits or wishes for a long life, or simply a something that catches the maker’s fancy! I’m not sure what dictated the maker’s choice of patterns for my new kinchaku, but it is stitched with a selection of five hitomezashi patterns, typical of the Shonai region in Yamagata prefecture. These are: two types of jujizashi (cross stitch), yamagata (mountain form), sanju kakinohanazashi (triple persimmon flower stitch) and kuchizashi (mouth stitch). I love the way the blocks merge without any border between them. And I am awed by the quality of stitching, which is just incredible! Every stitch is so perfectly aligned and neat you would almost think it was done by machine, but of course that is impossible. Owning this bag will certainly be an inspiration to me to up my game. I am almost embarrassed to post the picture of the one and only kinchaku that I’ve ever made. I find it very useful for holding all the thread, needles and tools together for whatever sashiko project I have on the go, but it’s such a handy item I often divert it for other purposes as well, so making more is on my list of items to do. In the meantime I have my lovely new kinchaku, but I don’t want to spoil it with knockabout use so I’m still deciding what to use it for. One thing I know; I will walk a little straighter when I carry this beautiful bag on me.
4 Comments
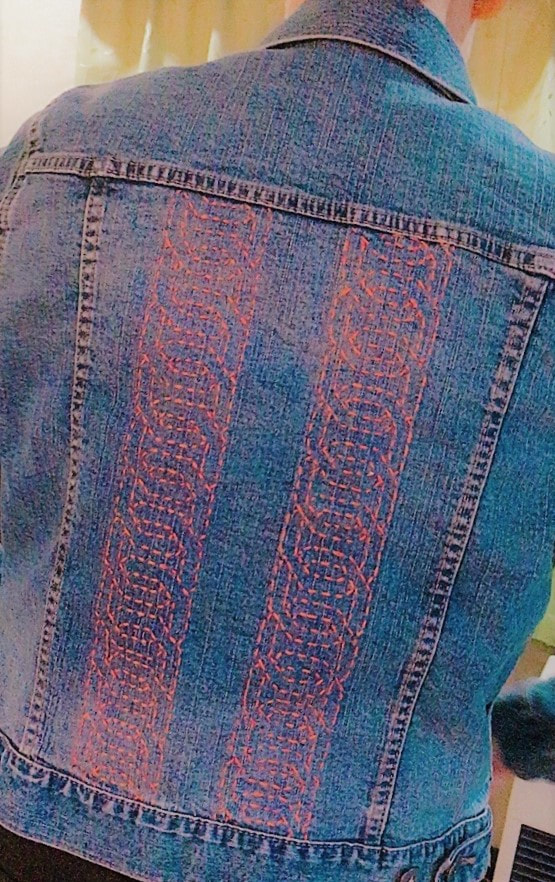
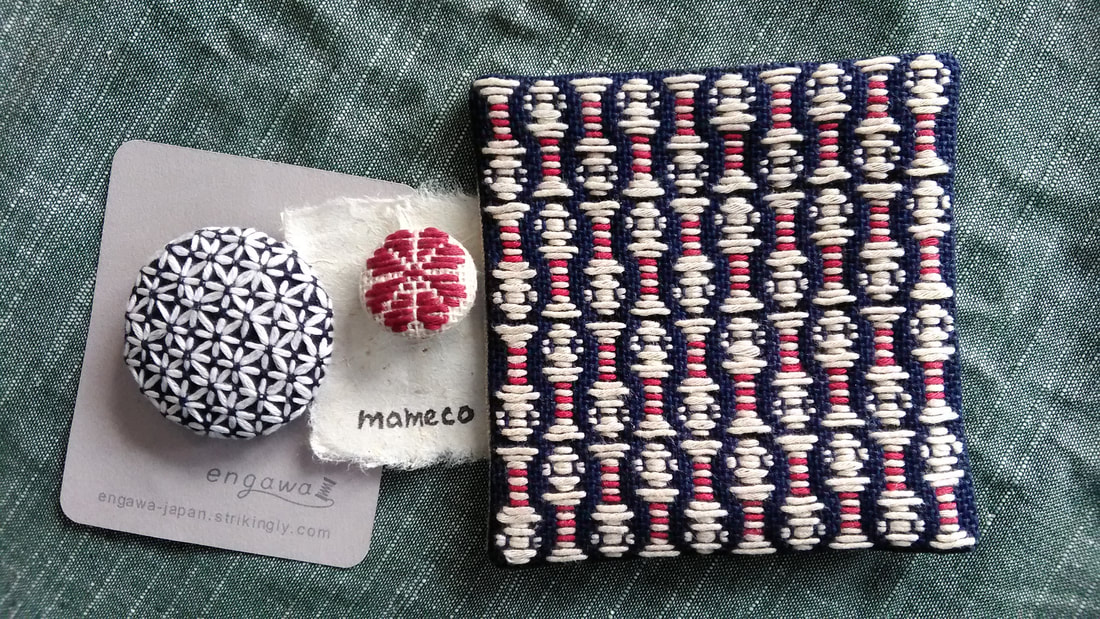
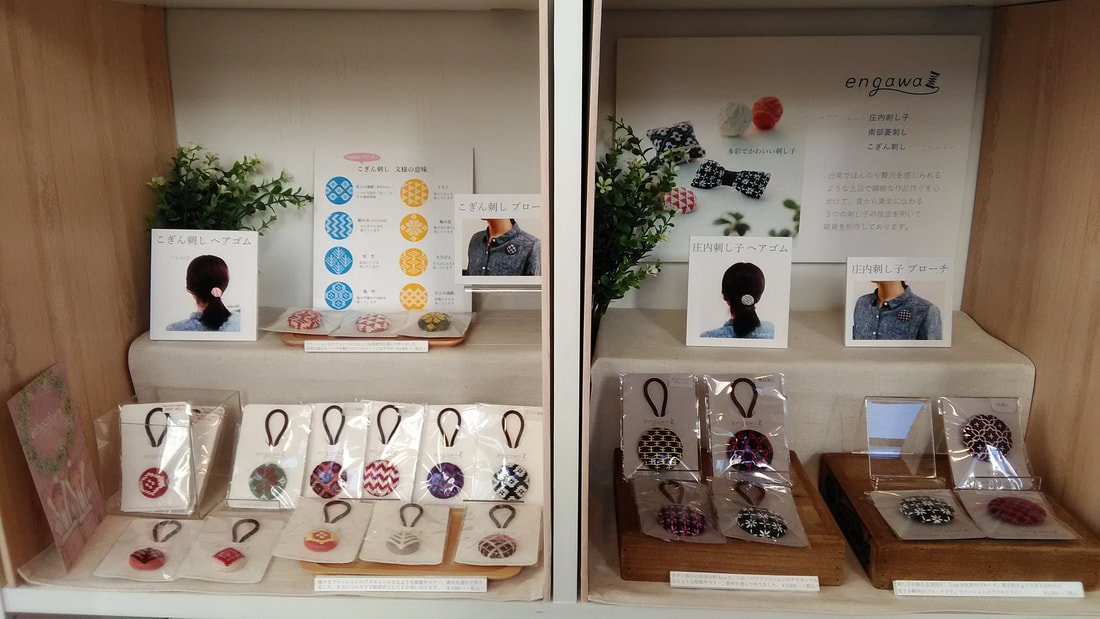
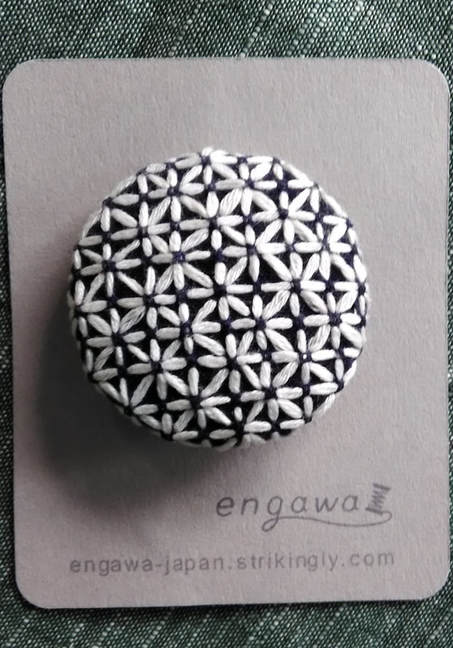
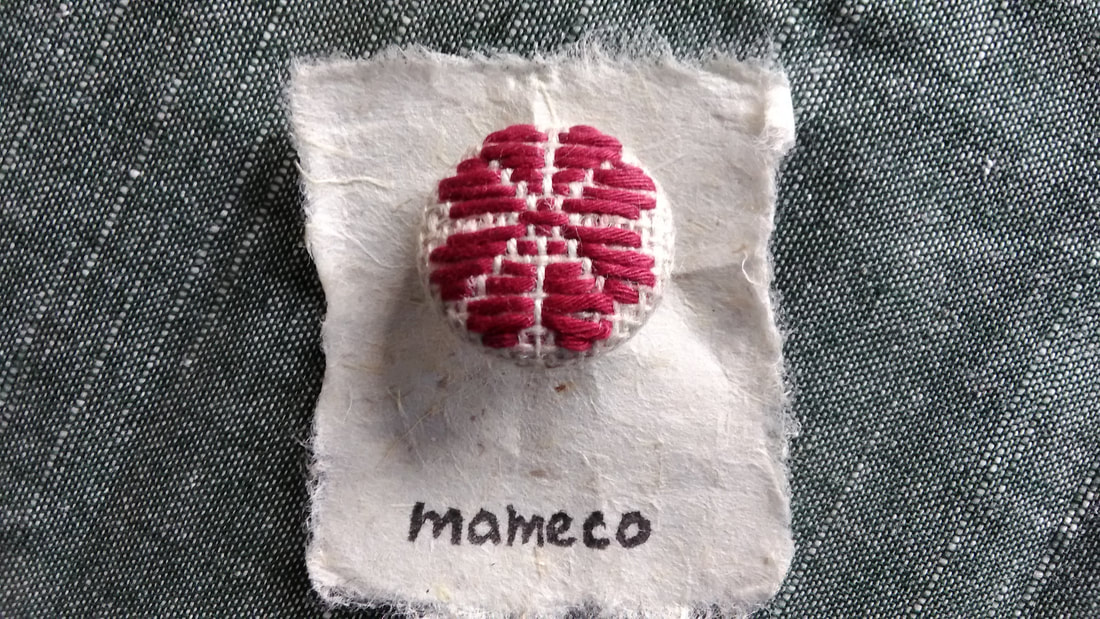
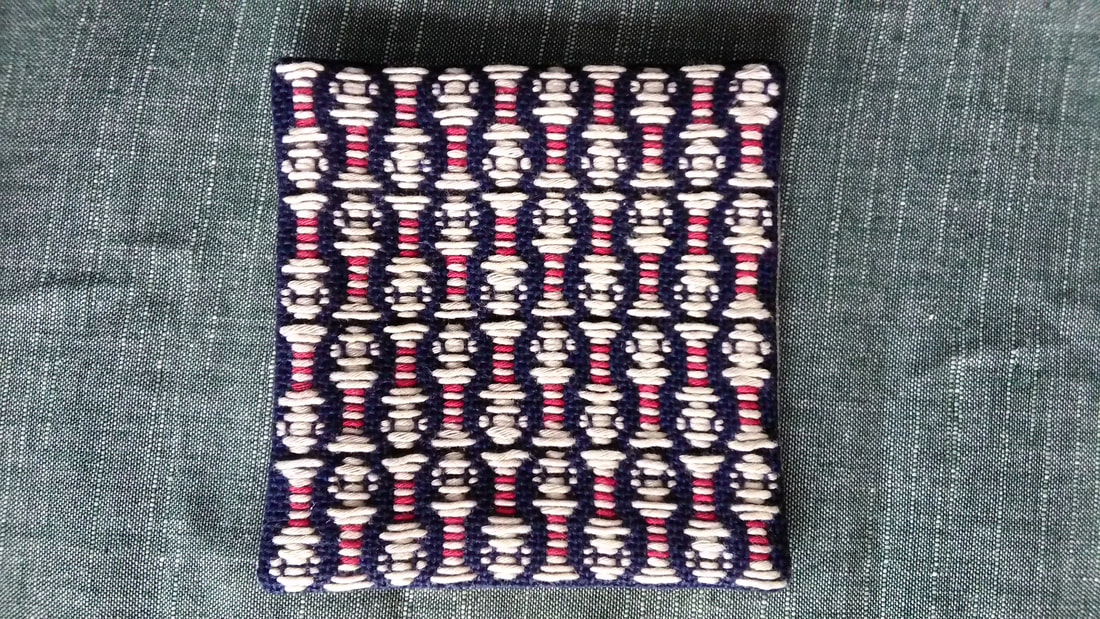
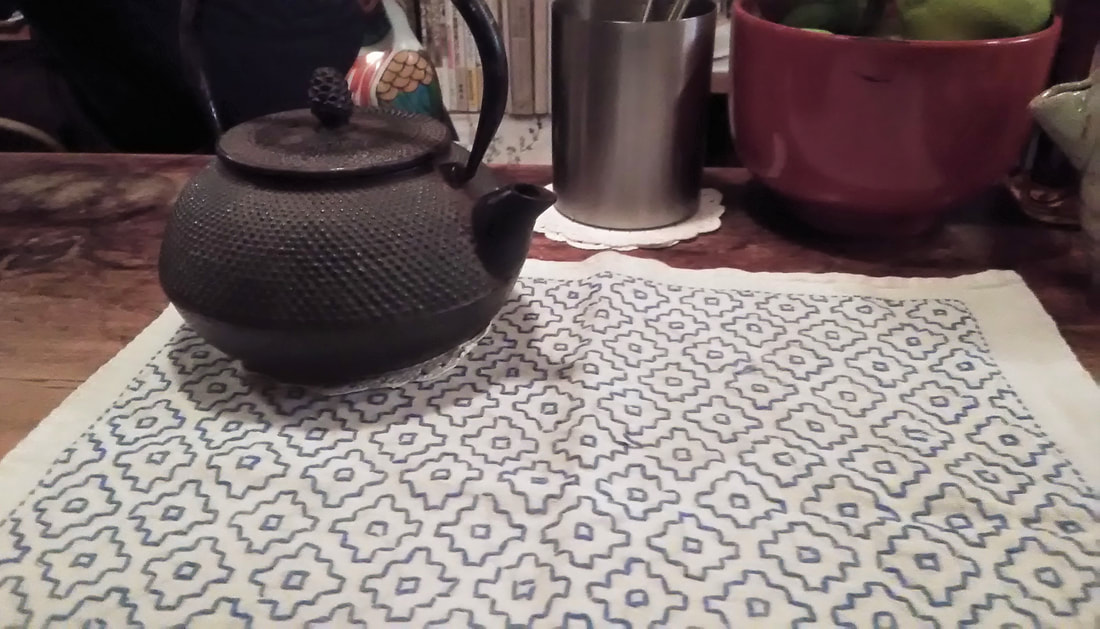
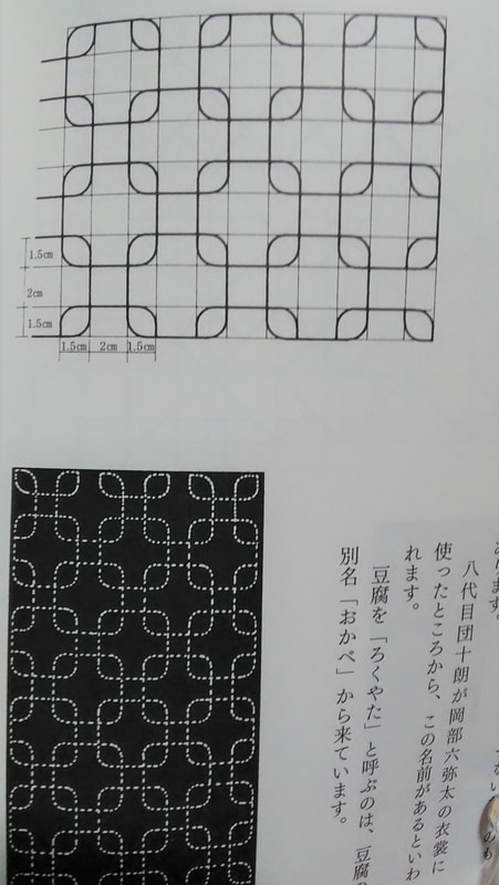
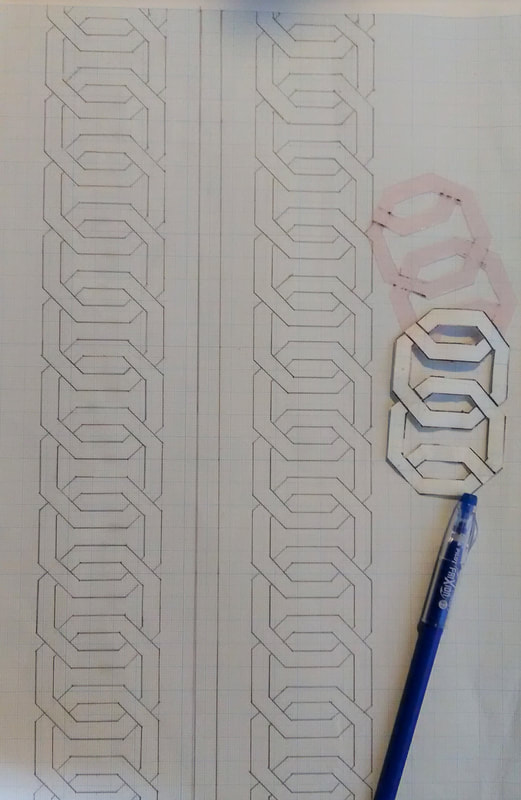
When I visited the Hida Sashiko exhibition last year I purchased a small book called Hida Sashiko no Techo (The Hida Sashiko Notebook, by Reiko Futatuya, first released in 1978, reprinted 2013, published by Hida Sashiko), as I always do whenever I come across a book about sashiko that’s not in my collection. Every book has its own appeal, and I never tire of looking through my collection and taking in the variety of sashiko styles and applications. Anyway, by today’s standards this book is very simple; thirty three pages in mostly black and white, and basically just a reference for patterns, but in 1978 when it was first published I doubt there were many books about sashiko available, so I am sure it would have been a valuable resource. (Still is, actually. I found it referred to less than a year ago on this blog, which is written in Japanese, but the photographs are lovely.) As with most such books there is a general description of sashiko’s roots in reusing and reinforcing cloth, but I liked the concrete examples given; for example stitching the tabi (socks) worn by the boatmen transporting lumber down the river to make the sole non-slip in the water; or stitching a chrysanthemum motif in the in the corner of a furoshiki (wrapping cloth) to prevent knots coming undone. There’s a brief discussion of cloth (hemp, cotton and silk), thread and needles, and tools with the general advice of choosing the thread and needles to suit your purpose. All in all there are twenty-eight designs introduced, which the author says are a sample of those most commonly used in Hida, and are a mixture of hitomezashi (one stitch), and moyozashi (pattern sashiko). Each design has a simple explanation of the name, composition and roots, and shows the dimensions on graph paper so that the patterns can be reproduced and adapted. Most of the patterns were familiar, as I had seen them before in various forms in other sashiko books, but I did find a couple that were completely new to me. One was Roku Yata goshi (Roku Yata lattice), so-called because it was used on the costume of a popular kabuki actor in the early 19th century when he played the role of a samurai called Roku Yata, and the pattern became hugely fashionable. Another was Yoshiwara tsunagi, (linked Yoshiwara) a series of linked octagons, which I have seen printed on towels and clothing but never as sashiko. According to this book it is often used for actors and dancers stage costumes. Further research led me to discover that it was used on the curtains of teahouses in the red-light Yoshiwara district in Edo, hence the name Yoshiwara. For some reason this design struck a chord in me; I love the suggestion of strength and complexity, in a compact simple line – and felt compelled to make something with it, so I stitched it onto the back of my jeans jacket. When Reiko Futatuya wrote that she hoped these patterns would be used for new fabrics and purposes, I don’t expect she imagined this! I was in Sendai recently with a couple of hours to spare, so I set out to see what I could find in the way of sashiko in the centre of the city. Sendai is the capital city of Miyagi Prefecture, part of the northern region of Japan known as Tohoku, where the three main types of sashiko originated. Shonai sashiko (of which hitomezashi is typical) comes from Yamagata prefecture, on the eastern border of Miyagi, while kogin sashiko and nanbu hishizashi originated in Aomori prefecture, which is north of Miyagi but with Iwate prefecture in between. I didn’t have to go very far to make my first discovery. Less than a hundred metres from my hotel I found TRY6, a community-sponsored business incubator shop for local entrepreneurs, where my eyes were immediately drawn to a couple of shelves with a beautiful display of small items such as brooches, buttons and hair-ties stitched with kogin and Shonai sashiko. These were the work of an artist whose needle name is engawa. I couldn’t resist buying a charming brooch of white komenohana zashi (rice flower) stitched on indigo-dyed cloth. According to engawa's website, s/he was born in Hokkaido, lives in Sendai, and has been stitching sashiko items since 2013. Take a look at this link (in Japanese) to see more of engawa’s delightful creations. “minne” and “creema”, by the way, are online Japanese shops. The helpful manager in TRY6 gave me a tip about another gallery he thought might have some sashiko, and sure enough when I reached the galerie arbre, I discovered the work of two more sashikoists. Kogin mameco, the needle name of a lady who specializes in kogin sashiko, had a lovely range of book covers, zip pouches and pencil cases on display. Once again, however, I couldn’t resist the brooches, and purchased a sweet button-sized brooch covered in a rough-weave beige cloth stitched with a red ume no hana (plum flower). See Kogin mameco’s work here. Hitomezashi and kogin sashiko are currently extremely popular in Japan, so I was not surprised that all the sashiko I had found so far was exclusively in those two styles. The sashikoist known as harinoto, who lives in Tochigi prefecture (which is not Tohoku) and whose work I also discovered in galerie arbre, however, was doing something quite original with kogin. Harinoto had made a series of coasters representing the six prefectures in Tohoku, stitched with a kogin-style motif emblematic of each prefecture. These were apples for Aomori, iron tea-pots for Iwate, woven straw horses for Akita, wooden kokeshi dolls for Miyagi, cherries for Yamagata, and toy red cows for Fukushima. Naturally I bought a kokeshi doll coaster as a souvenir of my visit to Miyagi. I tracked down harinoto’s blog and found that she has also published a book about kogin sashiko. Koginzashi moyo asobi (Playing around with kogin sashiko patterns) Nihon Vogue, 2016 (Amazon Japan affiliate link) All in all it was a very pleasant and satisfying way to while away a few hours, walking around the backstreets of Sendai in search of sashiko!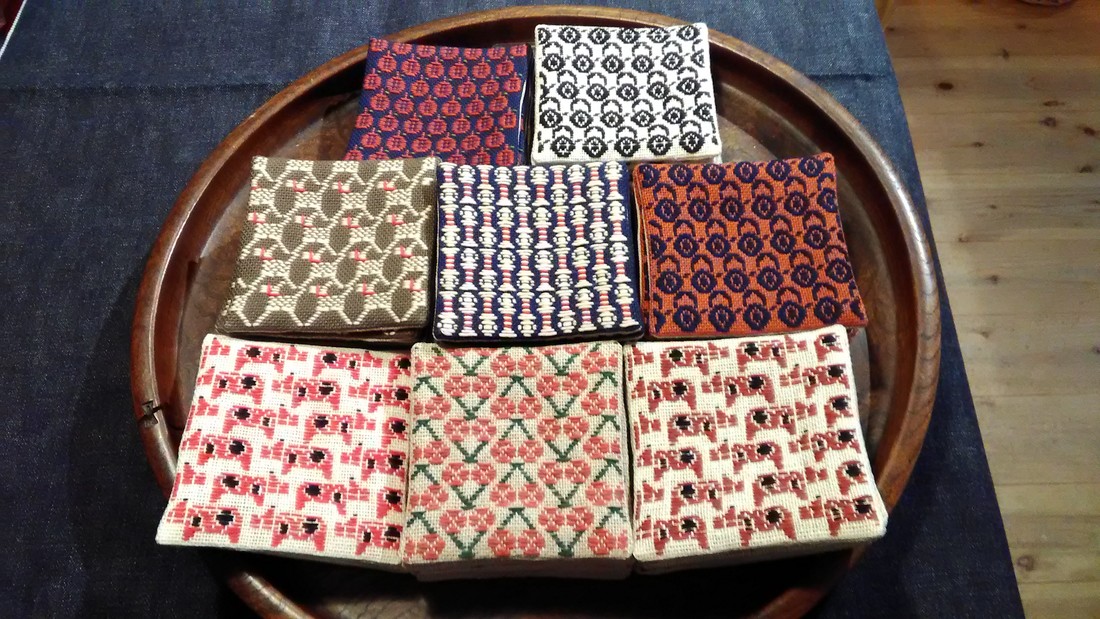  Coasters by harinoto Coasters by harinoto I’ve been busy getting the online shop ready and haven’t had much time for writing recently (or doing sashiko!), but here’s a review of a book I wanted to tell you about. Also, if you haven’t already ordered, don’t forget to take a look at the three-kit subscription set I’m taking orders for at the moment in my shop.. Anyway, the latest addition to my collection of sashiko books is this neat little volume published by Nihon Bungeisha in October. Sashiko no Teshigoto (Sashiko Handiwork - Amazon Japan affiliate link) is a collection of beautifully photographed fukin and other small handiwork items — such as a tissue box cover, purse, bag and coasters — with instructions on how to make them. As so often happens, when I bought this book and flicked through I immediately wanted to make everything, which of course I don’t have time for. But even if that’s not possible, I still get a lot of enjoyment from simply looking at photographs of beautiful sashiko stitching, and in that respect this book is very satisfying. It could easily be a coffee table book as the photography is lovely. The sashiko handiwork is displayed on mostly dark wood or light backgrounds, in tasteful minimalist settings with only an iron teapot or cane basket as an accent, and the overall effect is traditional yet modern, an accurate reflection of the sashiko items themselves: conventional but with an elegant, contemporary touch. For example, the white hanafukin with a cross flower stitch in charcoal grey, and one red flower in the corner. Or the chic tissue box cover with nagare hishizashi stitched in white on pale grey cotton. One reason I like this book is that it retains an emphasis on the traditional blue and white combination, while offering an updated version with subtle variations on that theme. As with many sashiko books it follows a standard format of introducing a number of sample pieces (in this case twenty), then providing samplers of the stitches, basic instructions on how to do sashiko (with explanations about cloth, thread, equipment, drafting, stitching and making two easy pieces), and instructions for making up each individual item. The stitches are introduced in four categories; straight line patterns such as tobi asanoha (scattered hemp leaf), curved line patterns such as fundo tsunagi (linked weights), hitomezashi such as kaki no hana (persimmon flower), and Shonai sashiko such as ganzezashi (sea urchin stitch). The last, ganzezashi, is one of my most favourite stitches. It could have something to do with the fact that sea urchin is my favourite sushi topping… but I also love the convergence of concentric lines that scream out to me sashiko! Stitched in white on blue cloth, this hanafukin is totally mesmerizing. Next to making it myself, a photograph is the next best thing.

Where has the time gone? While sashiko is never far from my mind, in this busy modern life it takes some planning to get me sitting in front of the computer long enough to actually write about it.
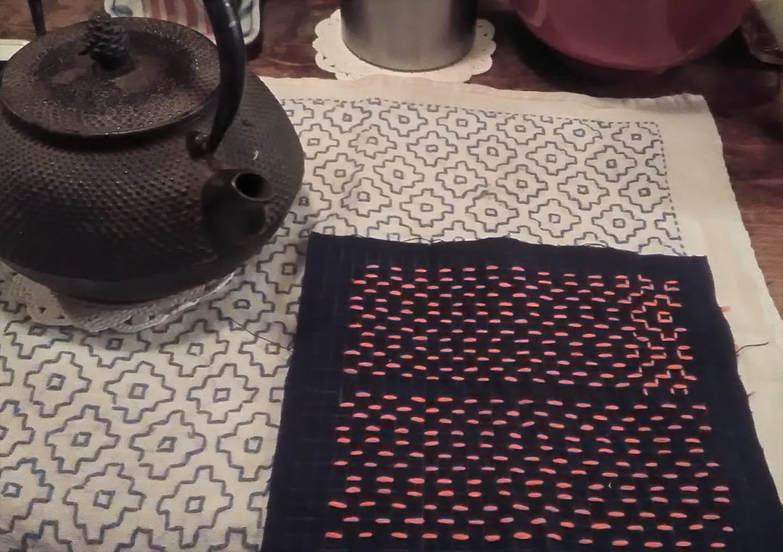
One tidbit of sashiko related news I wanted to tell you about was the announcement of the uniform for the Japanese soccer team in next year’s World Cup… featuring sashiko in the design. Next year will mark the twentieth anniversary since Japan first qualified to compete in the World Cup, so the concept is that sashiko will be the thread that connects up history. Isn’t that a nice idea! Speaking of sashiko connecting people, you may remember I previously wrote about visiting a tiny backstreet bar in Tokyo where the owner showed me hanafukin made by her 94-year-old mother-in-law (turns out it was mother-in-law, not mother). Well, the other day when I paid another visit I had a wonderful surprise; apparently the mother-in-law was so thrilled to hear about my visit, she sent me a little gift, two hanafukin that she had made. I was moved to tears, as never in my life did I expect to receive a hanafukin from my own mother, let alone anyone else’s! Another lovely surprise was that she had left me some other hanafukin to look at, one of which happened to be exactly the same pattern as the piece I was carrying around with me to work on, and my topic for today kaki no hana (persimmon flower).
This stitch is one kind of hitomezashi (one stitch sashiko), which you may recall I wrote before was traditionally often used for practical purposes, such as clothing or reinforcing material, because of the strength that the dense stitching imparts. Hitomezashi is typical of Shonai sashiko, one of the three major styles of sashiko. The Shonai region is Yamagata prefecture in northern Japan, a mountainous region, cold in winter, that faces the Japan Sea. The story goes that ships carried out regional products such as safflower and rice, and made the return journey with their holds filled with cotton and old clothing from the warmer regions they visited where cotton grew. Women would get busy stitching the cloth to make jackets, footwear and other useful items.
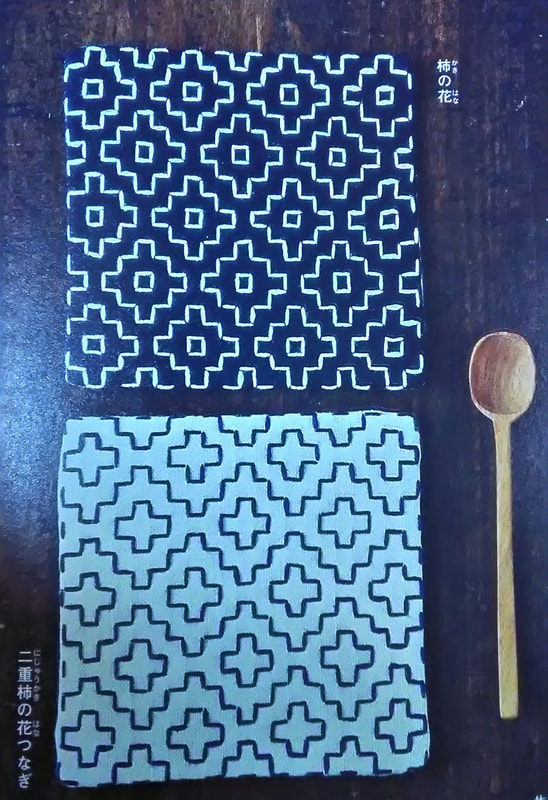
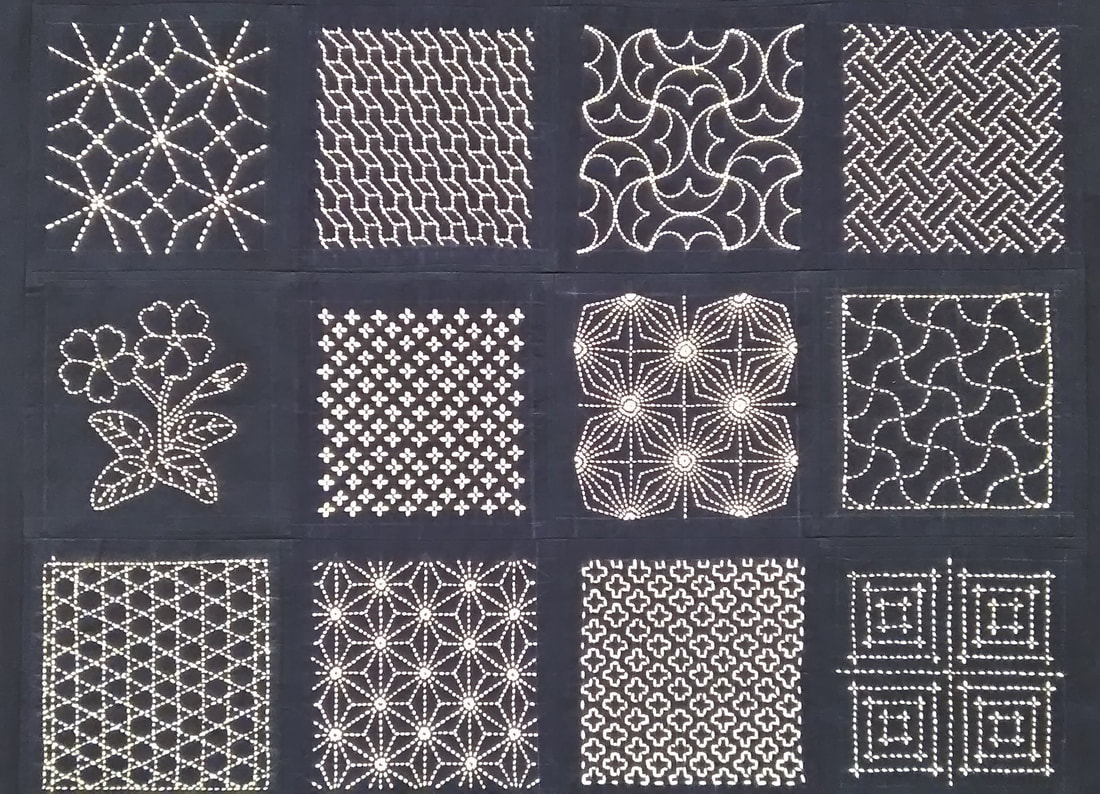
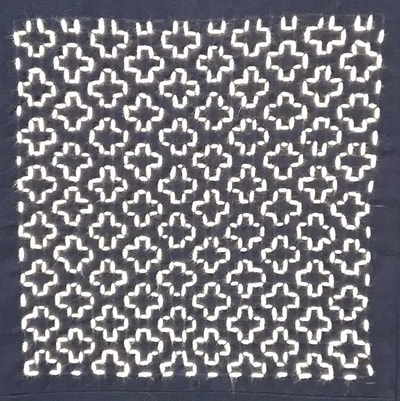
Compared to moyozashi (pattern stitches), I find hitomezashi easy in the sense that you don’t have to think about the length of your stitches or making them fit them the pattern, because each stitch is simply one side of a square in the grid. The only tricky thing is that you have to get the order of stitching right, if you don’t the pattern won’t appear. Transferring the pattern is simple too; just draw or trace a grid onto the fabric and off you go. The recommended size of the squares on the grid is 5mm, but they can be up to a centimeter. Any longer and the stitching will stick up or catch. Here’s some examples of kaki no hana stitching I found in my collection of sashiko books that may inspire you! (*Amazon Japan affiliate links included)
Above two images from Tohoku no Sashiko (Sashiko from the Tohoku region), Nihon Vogue-sha, 2016
Kawaii Hari Shigoto: Sashiko no Tezukurikomono (Charming Needlework: Small Handmade Sashiko Items), Boutique-sha, 2017
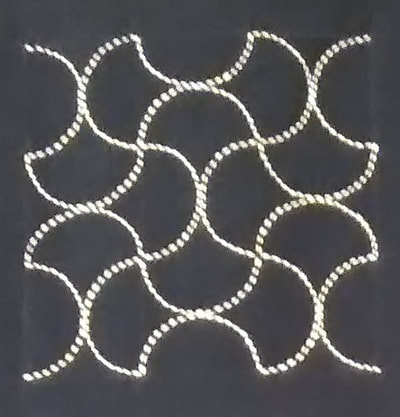
Last week my sashiko group participated in an annual exhibition held in the local Station Gallery. A train station might seem an unlikely location for a gallery, but actually it makes sense, as it’s the most central place in town and gets a lot of potential viewers passing by. Which happily was the case this time. 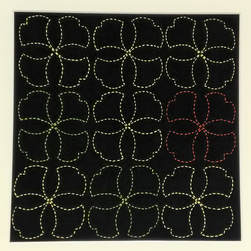 Icho tsunagi pattern (linked ginko leaves) Icho tsunagi pattern (linked ginko leaves) For the exhibition I decided to make another framed piece of sashiko to add to a series I started last year. This year I chose to stitch the pattern icho tsunagi, which means linked ginko leaves. As time was running short, I cheated by blowing up the pattern on a photocopier instead of enlarging the proportions on graph paper (shhh…don’t tell Sensei!). Then I cut and taped the paper pieces together to fit the cloth dimensions, taped chaco paper (transfer paper for tracing designs onto fabric) to the back of this pattern and traced over the design with a ballpoint pen to imprint it on the fabric. The autumn ginko leaves are gorgeous at this time of year and I wanted to reflect that by using thread in autumn colours of green and yellow, but unfortunately the result wasn’t as vivid as I hoped, so I ended up putting in one orange leaf for some contrast variation. Anyway, I was pleased with the result, and best of all Sensei praised my corner stitches. Phew! I didn’t want to let the side down… My fellow sashikoists all contributed their work from the past year and it was so exciting to see the inventive and wonderful pieces they’ve done all gathered in the one place. A real Aladdin”s cave! I had intended to describe these for you here, but realized I couldn’t possibly do them justice, so I’ll keep that for some later posts. The most thrilling exhibits, however, were the two wall hangings that were on display for the first time. Take a look at the amazing work below! These were the result of a joint project we’ve been working on all year, stitching squares fifteen by fifteen centimetres in length with whatever patterns we liked. When the time was up we gathered up all the squares and put them together to see what size hanging was possible. It turned out we had enough for two. Sensei gave no stipulations whatsoever as to what patterns we should stitch, but the overall balance seemed to be just right, and a lovely sampler of all the different styles of stitches; the densely stitched hitomezashi (single stitch), kyokusen moyozashi (curved line patterns), chokusen moyozashi (straight line patterns) and jiyuzashi (free stitching). I could look at these all day in wonder and never tire. What a gorgeous illustration of the beauty of sashiko!
Hello, welcome to my blog.
Let’s get this introductory stuff out of the way so we can get down to talking about the fun stuff as soon as possible! I was born in Australia and now reside long-term in Japan, working as a Japanese to English translator. And I'm a sashiko fanatic! I do sashiko because I love the patterns and learning about their history, thinking about colour combinations for fabric and thread, drawing up designs on graph paper and stitching them on the cloth. It’s like meditation, and better than resorting to any chemical option in my opinion. Nothing makes me more relaxed than when I’m stitching, or feel so satisfied as when I end up with a finished piece I can show off to my family and friends. If you’re reading this I’m sure you understand what I mean! I can’t sew and am really not very handy with doing craft projects generally, but I love sashiko, and I figure that if I can do it, anybody can. Several decades ago when I first came to Japan, it wasn’t very visible. I saw kits and was curious about this craft, but found very few books about it in Japanese let alone English. It’s a different story now, of course; sashiko is popular around the world (though many Japanese people can’t quite believe that!), the word is even recognized in English and there is a lot more literature available than there used to be. In fact, I think one of the best sashiko resource books available in any language is written in English not Japanese! The book I’m referring to Susan Briscoe’s The Ultimate Sashiko Sourcebook. But comparatively speaking, literature on sashiko still occupies only a small area of bookshelf space in the bookshops here, and Western-style stitching is more popular than sashiko. So it’s still not mainstream. I did kit pieces over the years to learn the stitches, but it was only after a life-changing illness a few years ago that I became seriously hooked and started drawing up designs myself. Nowadays I belong to a group and learn from a teacher. I’m still no expert at stitching, but I’m an addict, and my life is richer because of sashiko. My language skills give me access to all kinds of experiences in the sashiko world in Japan; meeting people, seeing exhibitions, and learning from books. This is the kind of thing that I’d like to share with you here in this blog: information about the contemporary sashiko scene in Japan that would be difficult to know about otherwise because of the language barrier. I hope you’ll join me on my adventures! |
Watts SashikoI love sashiko. I love its simplicity and complexity, I love looking at it, doing it, reading about it, and talking about it. Archives
September 2022
Categories
All
Sign up for the newsletter:
|
































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed



